Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Thyroid
- Frequency of TERT Promoter Mutations in Real-World Analysis of 2,092 Thyroid Carcinoma Patients
- Heera Yang, Hyunju Park, Hyun Jin Ryu, Jung Heo, Jung-Sun Kim, Young Lyun Oh, Jun-Ho Choe, Jung Han Kim, Jee Soo Kim, Hye Won Jang, Tae Hyuk Kim, Sun Wook Kim, Jae Hoon Chung
- Endocrinol Metab. 2022;37(4):652-663. Published online July 22, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2022.1477
- 3,667 View
- 194 Download
- 11 Web of Science
- 13 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Telomerase reverse transcriptase (TERT) promoter mutations are associated with increased recurrence and mortality in patients with thyroid carcinoma. Previous studies on TERT promoter mutations were retrospectively conducted on a limited number of patients.
Methods
We prospectively collected data on all consecutive patients who underwent thyroid carcinoma surgery between January 2019 and December 2020 at the Samsung Medical Center, Seoul, Korea. We included 2,092 patients with thyroid carcinoma.
Results
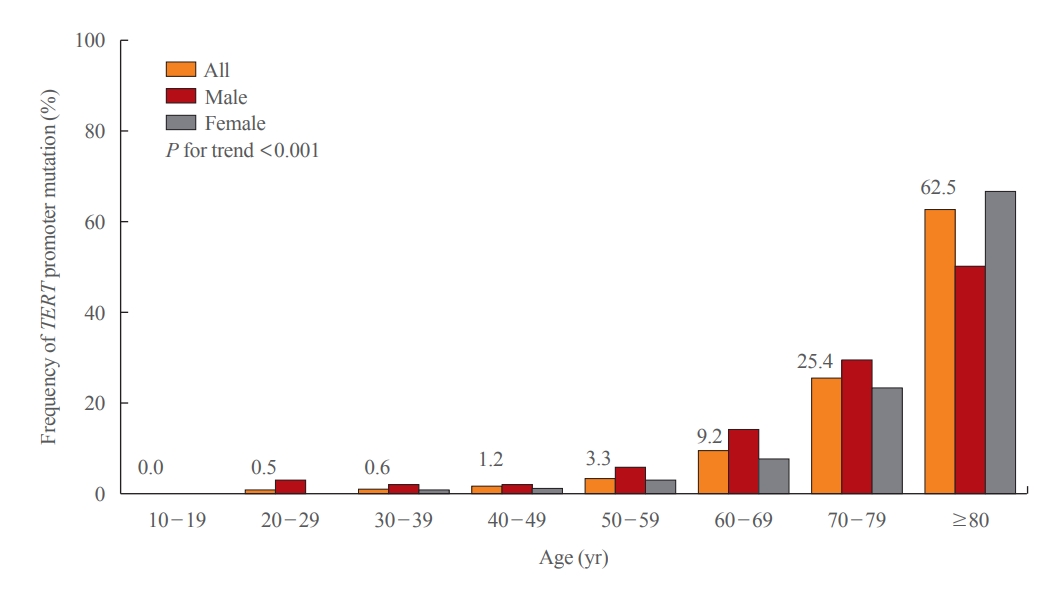
Of 2,092 patients, 72 patients (3.4%) had TERT promoter mutations. However, the frequency of TERT promoter mutations was 0.5% in papillary thyroid microcarcinoma (PTMC) ≤1 cm and it was 5.8% in papillary thyroid carcinoma (PTC) >1 cm. The frequency of TERT promoter mutations was significantly associated with older age at diagnosis (odds ratio [OR], 1.12; P<0.001), larger primary tumor size (OR, 2.02; P<0.001), and aggressive histological type (OR, 7.78 in follicular thyroid carcinoma; OR, 10.33 in poorly differentiated thyroid carcinoma; OR, 45.92 in anaplastic thyroid carcinoma; P<0.001). Advanced T stage, advanced N stage, and distant metastasis at diagnosis were highly prevalent in mutated thyroid cancers. However, initial distant metastasis was not present in patients with TERT promoter mutations in PTMC. Although the C228T mutation was more highly detected than the C250T mutation (64 cases vs. 7 cases), there were no significant clinicopathological differences.
Conclusion
This study is the first attempt to investigate the frequency of TERT promoter mutations in a real-world setting. The frequency of TERT promoter mutations in PTC was lower than expected, and in PTMC, young patients, and female patients, the frequency was very low. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by-
TERT Promoter Mutations Frequency Across Race, Sex, and Cancer Type
Talal El Zarif, Marc Machaalani, Rashad Nawfal, Amin H Nassar, Wanling Xie, Toni K Choueiri, Mark Pomerantz
The Oncologist.2024; 29(1): 8. CrossRef - Gene mutations as predictors of central lymph mode metastasis in cN0 PTC: A meta‐analysis
Jiaqi Ji, Xinlong Shi
Clinical Genetics.2024; 105(2): 130. CrossRef - Risk stratification by combining common genetic mutations and TERT promoter methylation in papillary thyroid cancer
Ye Sang, Guanghui Hu, Junyu Xue, Mengke Chen, Shubin Hong, Rengyun Liu
Endocrine.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Shortened telomere length in peripheral blood leukocytes is associated with cumulative radioactive iodine doses in patients with differentiated thyroid carcinoma
Hoonsung Choi, Sun Wook Cho, Hwan Hee Kim, Ka Hee Yi, Do Joon Park, Young Joo Park
Cancer.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - 2023 Update of the Korean Thyroid Association Guidelines for the Management of Thyroid Nodules
Eun Kyung Lee, Young Joo Park
Clinical Thyroidology®.2024; 36(4): 153. CrossRef - Deciphering the Functions of Telomerase Reverse Transcriptase in Head and Neck Cancer
Tsung-Jang Yeh, Chi-Wen Luo, Jeng-Shiun Du, Chien-Tzu Huang, Min-Hung Wang, Tzer-Ming Chuang, Yuh-Ching Gau, Shih-Feng Cho, Yi-Chang Liu, Hui-Hua Hsiao, Li-Tzong Chen, Mei-Ren Pan, Hui-Ching Wang, Sin-Hua Moi
Biomedicines.2023; 11(3): 691. CrossRef - 2023 Korean Thyroid Association Management Guidelines for Patients with Thyroid Nodules
Young Joo Park, Eun Kyung Lee, Young Shin Song, Soo Hwan Kang, Bon Seok Koo, Sun Wook Kim, Dong Gyu Na, Seung-Kuk Baek, So Won Oh, Min Kyoung Lee, Sang-Woo Lee, Young Ah Lee, Yong Sang Lee, Ji Ye Lee, Dong-Jun Lim, Leehi Joo, Yuh-Seog Jung, Chan Kwon Jung
International Journal of Thyroidology.2023; 16(1): 1. CrossRef - Thyroid Cancer, Iodine, and Gene Mutation
Jae Hoon Chung
International Journal of Thyroidology.2023; 16(1): 89. CrossRef - Mortality rate and causes of death in papillary thyroid microcarcinoma
Jung Heo, Hyun Jin Ryu, Hyunju Park, Tae Hyuk Kim, Sun Wook Kim, Young Lyun Oh, Jae Hoon Chung
Endocrine.2023; 83(3): 671. CrossRef - TERT promoter mutations in thyroid cancer
Michiko Matsuse, Norisato Mitsutake
Endocrine Journal.2023; 70(11): 1035. CrossRef - TERT Promoter and BRAF V600E Mutations in Papillary Thyroid Cancer: A Single-Institution Experience in Korea
Min Jhi Kim, Jin Kyong Kim, Gi Jeong Kim, Sang-Wook Kang, Jandee Lee, Jong Ju Jeong, Woong Youn Chung, Daham Kim, Kee-Hyun Nam
Cancers.2022; 14(19): 4928. CrossRef - Frequency of TERT Promoter Mutations in Real-World Analysis of 2,092 Thyroid Carcinoma Patients (Endocrinol Metab 2022;37:652-63, Heera Yang et al.)
Hyunju Park, Jae Hoon Chung
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2022; 37(6): 949. CrossRef - Frequency of TERT Promoter Mutations in Real-World Analysis of 2,092 Thyroid Carcinoma Patients (Endocrinol Metab 2022;37:652-63, Heera Yang et al.)
Sue Youn Kim, Chan Kwon Jung
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2022; 37(6): 947. CrossRef
-
TERT Promoter Mutations Frequency Across Race, Sex, and Cancer Type

- Adrenal gland
- Bilateral Adrenocortical Masses Producing Aldosterone and Cortisol Independently
- Seung-Eun Lee, Jae Hyeon Kim, You-Bin Lee, Hyeri Seok, In Seub Shin, Yeong Hee Eun, Jung-Han Kim, Young Lyun Oh
- Endocrinol Metab. 2015;30(4):607-613. Published online December 31, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2015.30.4.607
- 4,151 View
- 46 Download
- 5 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader A 31-year-old woman was referred to our hospital with symptoms of hypertension and bilateral adrenocortical masses with no feature of Cushing syndrome. The serum aldosterone/renin ratio was elevated and the saline loading test showed no suppression of the plasma aldosterone level, consistent with a diagnosis of primary hyperaldosteronism. Overnight and low-dose dexamethasone suppression tests showed no suppression of serum cortisol, indicating a secondary diagnosis of subclinical Cushing syndrome. Adrenal vein sampling during the low-dose dexamethasone suppression test demonstrated excess secretion of cortisol from the left adrenal mass. A partial right adrenalectomy was performed, resulting in normalization of blood pressure, hypokalemia, and high aldosterone level, implying that the right adrenal mass was the main cause of the hyperaldosteronism. A total adrenalectomy for the left adrenal mass was later performed, resulting in a normalization of cortisol level. The final diagnosis was bilateral adrenocortical adenomas, which were secreting aldosterone and cortisol independently. This case is the first report of a concurrent cortisol-producing left adrenal adenoma and an aldosterone-producing right adrenal adenoma in Korea, as demonstrated by adrenal vein sampling and sequential removal of adrenal masses.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Different cell compositions and a novel somatic KCNJ5 variant found in a patient with bilateral adrenocortical adenomas secreting aldosterone and cortisol
Liling Zhao, Jinjing Wan, Yujun Wang, Wenjun Yang, Qi Liang, Jinrong Wang, Ping Jin
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Adrenal Vein Cortisol to Metanephrine Ratio for Localizing ACTH-Independent Cortisol-Producing Adenoma: A Case Report
Rishi Raj, Philip A Kern, Neelima Ghanta, Edilfavia M Uy, Kamyar Asadipooya
Journal of the Endocrine Society.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Adrenal Venous Sampling for Subtype Diagnosis of Primary Hyperaldosteronism
Mitsuhide Naruse, Akiyo Tanabe, Koichi Yamamoto, Hiromi Rakugi, Mitsuhiro Kometani, Takashi Yoneda, Hiroki Kobayashi, Masanori Abe, Youichi Ohno, Nobuya Inagaki, Shoichiro Izawa, Masakatsu Sone
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2021; 36(5): 965. CrossRef - Hypercortisolism and primary aldosteronism caused by bilateral adrenocortical adenomas: a case report
Kaiyun Ren, Jia Wei, Qilin Liu, Yuchun Zhu, Nianwei Wu, Ying Tang, Qianrui Li, Qianying Zhang, Yerong Yu, Zhenmei An, Jing Chen, Jianwei Li
BMC Endocrine Disorders.2019;[Epub] CrossRef
- Different cell compositions and a novel somatic KCNJ5 variant found in a patient with bilateral adrenocortical adenomas secreting aldosterone and cortisol

- Thyroid
- The Validity of Ultrasonography-Guided Fine Needle Aspiration Biopsy in Thyroid Nodules 4 cm or Larger Depends on Ultrasonography Characteristics
- Jin Hwa Kim, Na Kyung Kim, Young Lyun Oh, Hye Jeong Kim, Sang Yong Kim, Jae Hoon Chung, Sun Wook Kim
- Endocrinol Metab. 2014;29(4):545-552. Published online December 29, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2014.29.4.545
- 3,715 View
- 31 Download
- 9 Web of Science
- 9 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background The objective of this study was to evaluate the validity of fine needle aspiration biopsy (FNAB) according to ultrasonography (US) characteristics in thyroid nodules 4 cm and larger.
Methods We retrospectively reviewed the cases of 263 patients who underwent thyroid surgery for thyroid nodules larger than 4 cm between January 2001 and December 2010.
Results The sensitivity of US-FNAB was significantly higher in nodules with calcifications (micro- or macro-) than those without (97.9% vs. 87.%
P <0.05). The accuracy of US-FNAB was higher in large thyroid nodules with US features suspicious of malignancy, such as a solid component, ill-defined margin, hypoechogenicity or marked hypoechogenicity, or any calcifications (micro- or macro-) compared to thyroid nodules with none of these features. Furthermore, the accuracy improved as the number of these features increased. The overall false negative rate (FNR) was 11.9%. The FNR of thyroid nodules that appeared benign on US, such as mixed nodules (7.7%) or nodules without calcification (9.8%), trended toward being lower than that of solid nodules (17.9%) or nodules with any microcalcification or macrocalcification (33.3%). In nodules without suspicious features of malignancy, the FNR of US-FNAB was 0% (0/15).Conclusion We suggest individualized strategies for large thyroid nodules according to US features. Patients with benign FNAB can be followed in the absence of any malignant features in US. However, if patients exhibit any suspicious features, potential false negative results of FNAB should be kept in mind and surgery may be considered.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Risk of malignancy and diagnostic accuracy of fine-needle aspiration biopsy in thyroid nodules with diameters greater than 4 centimeters
Rafaela N. Barcelos, Cléber P. Camacho, Maria da Conceição de O. C. Mamone, Elza S. Ikejiri, Felipe A. B. Vanderlei, Ji H. Yang, Rosália P. Padovani, Leandro A. L. Martins, Rosa Paula M. Biscolla, Danielle Macellaro, Susan C. Lindsey, Rui M. B. Maciel, Jo
Archives of Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The comparison of accuracy of ultrasonographic features versus ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration cytology in diagnosis of malignant thyroid nodules
Mehrdad Nabahati, Zoleika Moazezi, Soude Fartookzadeh, Rahele Mehraeen, Naser Ghaemian, Majid Sharbatdaran
Journal of Ultrasound.2019; 22(3): 315. CrossRef - False negative rate of fine‐needle aspiration in thyroid nodules: impact of nodule size and ultrasound pattern
Hye Shin Ahn, Dong Gyu Na, Jung Hwan Baek, Jin Yong Sung, Ji‐Hoon Kim
Head & Neck.2019; 41(4): 967. CrossRef - Thyroid nodules over 4 cm do not have higher malignancy or benign cytology false-negative rates
Muhammed Kizilgul, Rupendra Shrestha, Angela Radulescu, Maria R. Evasovich, Lynn A. Burmeister
Endocrine.2019; 66(2): 249. CrossRef - Large Cytologically Benign Thyroid Nodules Do Not Have High Rates of Malignancy or False-Negative Rates and Clinical Observation Should be Considered: A Meta-Analysis
Nicole A. Cipriani, Michael G. White, Peter Angelos, Raymon H. Grogan
Thyroid.2018; 28(12): 1595. CrossRef - Risk of Malignancy in Thyroid Nodules 4 cm or Larger
Uchechukwu C. Megwalu
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2017; 32(1): 77. CrossRef - Usefulness of NRAS codon 61 mutation analysis and core needle biopsy for the diagnosis of thyroid nodules previously diagnosed as atypia of undetermined significance
Eun Kyung Jang, Won Gu Kim, Eui Young Kim, Hyemi Kwon, Yun Mi Choi, Min Ji Jeon, Jung Hwan Baek, Jeong Hyun Lee, Tae Yong Kim, Young Kee Shong, Jene Choi, Dong Eun Song, Won Bae Kim
Endocrine.2016; 52(2): 305. CrossRef - Association between neck ultrasonographic findings and clinico‐pathological features in the follicular variant of papillary thyroid carcinoma
Eun Kyung Jang, Won Gu Kim, Yun Mi Choi, Min Ji Jeon, Hyemi Kwon, Jung Hwan Baek, Jeong Hyun Lee, Tae Yong Kim, Young Kee Shong, Dong Eun Song, Won Bae Kim
Clinical Endocrinology.2015; 83(6): 968. CrossRef - Articles in 'Endocrinology and Metabolism' in 2014
Won-Young Lee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2015; 30(1): 47. CrossRef
- Risk of malignancy and diagnostic accuracy of fine-needle aspiration biopsy in thyroid nodules with diameters greater than 4 centimeters

- Frequency of RAS Mutations and PAX8/PPARgamma Rearrangement in Follicular Thyroid Tumors in Korea.
- Hye Jeong Kim, Hye Won Jang, Seo Young Sohn, Yoon La Choi, Hee Jin Kim, Young Lyun Oh, Sun Wook Kim, Jae Hoon Chung
- Endocrinol Metab. 2012;27(1):45-53. Published online March 1, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2012.27.1.45
- 22,703 View
- 22 Download
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
Follicular thyroid tumors harbor several genetic alterations such as RAS mutations and PAX8/PPARgamma rearrangement. The aims of our study were to investigate the prevalence of RAS mutations and PAX8/PPARgamma rearrangement in follicular thyroid tumors and to correlate RAS mutations and/or PAX8/PPARgamma rearrangement with clinicopathologic features in Korean patients with follicular thyroid carcinomas. METHODS: RAS mutations were investigated by polymerase chain reaction and DNA sequencing in surgical specimens of 37 follicular thyroid carcinomas (FTCs) and 16 follicular thyroid adenomas (FTAs). PAX8/PPARgamma rearrangement was analyzed by fluorescent in situ hybridization in surgical specimens of 31 FTCs and 13 FTAs. RESULTS: RAS mutations were detected in 30% (11 of 37) of FTCs and 19% (three of 16) of FTAs. Three of 11 FTC patients with RAS mutations died of thyroid cancer, but none of the 26 FTC patients without RAS mutations. PAX8/PPARgamma rearrangement was found in 10% (three of 31) of FTCs, but in none of the 13 FTAs. All three FTC patients with PAX8/PPARgamma rearrangement remained in complete remission during follow-up. There were no FTC patients with both RAS mutations and PAX8/PPARgamma rearrangement. CONCLUSION: The prevalence of RAS mutations in our series of follicular tumors was similar to previous studies. The frequency of PAX8/PPARgamma rearrangements in our group of FTC was lower than previous western reports, but higher than Japanese reports. RAS mutations may be associated with hematogeneous metastasis and poor survival while PAX8/PPARgamma rearrangement may be related to more favorable prognosis in Korean patients with FTCs. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Preoperative serum thyroglobulin and changes in serum thyroglobulin during TSH suppression independently predict follicular thyroid carcinoma in thyroid nodules with a cytological diagnosis of follicular lesion
Hye Jeong Kim, Ji-Oh Mok, Chul Hee Kim, Yeo Joo Kim, Sang Jin Kim, Hyeong Kyu Park, Dong Won Byun, Kyoil Suh, Myung Hi Yoo
Endocrine Research.2017; 42(2): 154. CrossRef - Mutation Profile of Well-Differentiated Thyroid Cancer in Asians
Young Shin Song, Jung Ah Lim, Young Joo Park
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2015; 30(3): 252. CrossRef - Analysis of RAS mutation and PAX8/PPARγ rearrangements in follicular-derived thyroid neoplasms in a Korean population: frequency and ultrasound findings
S. H. Jeong, H. S. Hong, J. J. Kwak, E. H. Lee
Journal of Endocrinological Investigation.2015; 38(8): 849. CrossRef
- Preoperative serum thyroglobulin and changes in serum thyroglobulin during TSH suppression independently predict follicular thyroid carcinoma in thyroid nodules with a cytological diagnosis of follicular lesion

- Clinical Differences between Classic Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma and Variants.
- Ji Young Park, Ji In Lee, Alice Hyun Kyung Tan, Hye Won Jang, Hyun Won Shin, Young Lyun Oh, Jung Hee Shin, Jung Han Kim, Ji Soo Kim, Young Ik Son, Sun Wook Kim, Jae Hoon Chung
- J Korean Endocr Soc. 2009;24(3):165-173. Published online September 1, 2009
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/jkes.2009.24.3.165
- 2,051 View
- 22 Download
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
The outcomes of papillary thyroid carcinoma (PTC) variants have been described in a limited number of studies. The purpose of this study was to compare patient outcomes of PTC variants with those of patients with classic PTC. METHODS: A single-institution retrospective analysis was performed to review 2,366 patients with classic PTC and 159 patients with PTC variants diagnosed between 1994 and 2004. PTC variant patients were divided into two groups, favorable (n = 119, 119 follicular variants including 14 encapsulated follicular variants) and aggressive (n = 40, including 13 diffuse sclerosing, 11 tall cell, six solid, six oncocytic, and four columnar cell variants). RESULTS: Compared with classic PTC, the favorable and aggressive variants had a significantly larger tumor size (P<0.001). The favorable variants had significantly lower rates of bilaterality, multifocality, extrathyroidal invasion, cervical lymph node metastasis, stage III and IV disease, and greater male to female ratio (P<0.05). In particular, the encapsulated follicular variant showed no bilaterality, multifocality, extrathyroidal invasion, lymph node metastasis, and distant metastasis. However, the disease-specific survival and recurrence-free survival of patients with favorable PTC were not different from the patients with classic PTC. The aggressive variants had significantly higher rates of bilaterality and cervical lymph node metastasis compared to the classic PTC (P<0.05). They had significantly reduced disease-specific survival and recurrence-free survival rates (P<0.01). CONCLUSIONS: Knowledge of the nature of PTC variants, especially aggressive types, is important in predicting patient outcome and providing appropriate treatment. Further study is needed to better understand PTC variants. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Ultrasonographic Characteristics of the Follicular Variant Papillary Thyroid Cancer According to the Tumor Size
Eon Ju Jeon, Young Ju Jeong, Sung Hwan Park, Chang Ho Cho, Ho Sang Shon, Eui Dal Jung
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2016; 31(3): 397. CrossRef - Follicular Variant of Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma: Distinct Biologic Behavior Based on Ultrasonographic Features
Sun Jung Rhee, Soo Yeon Hahn, Eun Sook Ko, Jae Wook Ryu, Eun Young Ko, Jung Hee Shin
Thyroid.2014; 24(4): 683. CrossRef
- Ultrasonographic Characteristics of the Follicular Variant Papillary Thyroid Cancer According to the Tumor Size

- A Case of Hyalinizing Trabecular Adenoma of the Thyroid Gland.
- Hyun Won Shin, Young Lyun Oh, Hye Won Jang, Ji In Lee, Sun Wook Kim, Yong Ki Min, Myung Shik Lee, Moon Kyu Lee, Kwang Won Kim, Jae Hoon Chung
- J Korean Endocr Soc. 2009;24(1):54-57. Published online March 1, 2009
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/jkes.2009.24.1.54
- 2,062 View
- 19 Download
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Hyalinizing trabecular tumor is a rare benign thyroid tumor first described by Carney et al. in 1987. The tumor is characterized by an encapsulated nodule, trabecular arrangement of polygonal, oval, elongated cells, and hyalinized stroma. It is easily confused with papillary thyroid carcinoma or medullary thyroid carcinoma on surgical and cytologic specimens. A 45-year-old man presented with an incidentally detected left thyroid mass. Fine needle aspiration was performed and papillary thyroid carcinoma was suspected. However, the surgical specimen revealed a hyalinizing trabecular adenoma. We present this hyalinizing trabecular adenoma case to share our experience with physicians and specialists.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A Case of Multifocal Hyalinizing Trabecular Tumors of the Thyroid
Gland
Suhwan Jeong, Hanaro Park
Journal of Clinical Otolaryngology Head and Neck Surgery.2021; 32(3): 308. CrossRef - A Case of Hyalinizing Trabecular Tumor of the Thyroid Gland
Kun Woo Kim, Sang Joon Lee, Phil-Sang Chung, Junghwan Moon
Korean Journal of Otorhinolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery.2012; 55(12): 795. CrossRef
- A Case of Multifocal Hyalinizing Trabecular Tumors of the Thyroid
Gland

- Solitary Papillary Thyroid Microcarcinoma (0.3 cm in Diameter) Presenting Multiple Distant Metastases at the Time of Diagnosis.
- Tae Hyun Kim, Jung Han Kim, Young Lyun Oh, You Cheol Hwang, Jung Hwa Jung, Hye Seung Jung, Mira Kang, Yong Ki Min, Myung Shik Lee, Moon Kyu Lee, Kwang Won Kim, Jae Hoon Chung
- J Korean Endocr Soc. 2007;22(4):287-291. Published online August 1, 2007
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/jkes.2007.22.4.287
- 2,217 View
- 17 Download
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Papillary thyroid microcarcinoma (PTMC) is defined as being 1 cm or less in diameter. Although the prognosis of PTMC is known to be more favorable than that of papillary thyroid carcinoma greater than 1 cm in diameter, pathologic factors suggesting aggressiveness, such as multifocality and lymph node invasion, have been reported to be highly prevalent in PTMC. However, the rate of distant metastasis in patients with PTMC is very low. Many investigators have reported that initial distant metastasis was detected only in patients with PTMC greater than 0.4 cm in diameter, however these cases have involved only one organ, usually the lung. We report here on an extremely unusual case of solitary PTMC (0.3 cm in diameter) presenting multiple distant metastases at the time of diagnosis.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Clinico-pathologic Characteristics of the Primary Thyroid Cancer in Patients with Breast Cancer
Hyun Won Shin, Hye Won Jang, Ji Young Park, Jae Hoon Chung, Young-Ki Min, Myung-Shik Lee, Moon-Kyu Lee, Kwang-Won Kim, Sun Wook Kim
Journal of Korean Endocrine Society.2009; 24(4): 240. CrossRef
- Clinico-pathologic Characteristics of the Primary Thyroid Cancer in Patients with Breast Cancer

- ras Mutation in Korean Papillary Thyroid Carcinomas.
- Jung Hwa Jung, Keun Sook Kim, Tae Sik Jung, Young Lyun Oh, Hye Won Jang, Hye Seung Jung, Yong Ki Min, Myung Shik Lee, Moon Kyu Lee, Kwang Won Kim, Jae Hoon Chung
- J Korean Endocr Soc. 2007;22(3):203-209. Published online June 1, 2007
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/jkes.2007.22.3.203
- 1,838 View
- 17 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
RET/PTC rearrangement and mutations of BRAF and ras are well-known oncogenes involved in the pathogenesis of papillary thyroid carcinoma (PTC). The prevalence of RET/PTC rearrangement and BRAF mutations were 0~13% and 66~83% in Korean patients with PTC, respectively. We evaluated the prevalence of ras mutations in surgical specimens of PTC, and we compared them with the patients' clinical features. SUBJECTS AND METHODS: We included the surgical specimens of 49 PTCs and a few follicular thyroid carcinomas (FTCs) and follicular adenomas (FAs) as positive controls. Polymerase chain reaction, single strand conformation polymorphism and direct sequence analysis were consecutively performed to detect ras mutations. RESULTS: No mutations of the ras oncogenes were detected in 49 PTCs. However, heterozygous mutations of the ras oncogenes were found in a FTC and FA as positive controls, respectively. CONCLUSION: These findings suggested that ras mutation is not or rarely related to the tumorigenesis of PTCs in Koreans. Therefore, BRAF mutations and RET/PTC rearrangement, rather than ras mutation, might contribute the development of PTC in Koreans.

- p53, p21 and bcl-2 Protein Expressions and the Clinical Significance in Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma.
- Tae Sik Jung, Keun Sook Kim, Young Lyun Oh, Jung Hwa Jung, Eun Young Lee, Hye Seung Jung, Yong Ki Min, Myung Shik Lee, Moon Kyu Lee, Kwang Won Kim, Jae Hoon Chung
- J Korean Endocr Soc. 2007;22(2):98-104. Published online April 1, 2007
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/jkes.2007.22.2.98
- 1,842 View
- 18 Download
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
There have been some investigations concerning the role of p53, p21 and bcl-2 protein expressions for the tumorigenesis of thyroid cancer. It had been debated that these protein expressions were associated with aggressive features of papillary thyroid carcinoma. We studied to evaluate the prevalence of these protein expressions and their clinical significances in papillary thyroid carcinoma. METHODS: We selected 49 patients with papillary thyroid carcinoma who had been operated on at Samsung Medical Center during the last 10 years. Immunohistochemical staining for p53, p21 and bcl-2 was done by the use of paraffin embedded tissues. We analyzed the results of immunohistochemical staining for p53, p21 and bcl-2 and the correlation with the patients' age, gender, tumor size, multifocality, tumor invasion to both lobes, extrathyroidal invasion, cervical lymph node invasion, distant metastasis and the clinical outcomes. RESULTS: Immunohistochemical staining for p53 was positive in 10 patients (20%), p21 was positive in 36 patients (73%) and bcl-2 was positive in 18 patients (37%). The p53 and bcl-2 expressions were not associated with the clinical parameters. Tumor multifocality and extrathyroidal invasion were significantly higher in the p21 positive group (both P < 0.05). CONCLUSION: This study showed that the p21 protein expression was associated with tumor multifocality and extrathyroidal invasion in the patients with papillary thyroid carcinoma. Immunohistochemical stains for p21 may be used as a parameter for tumor aggressiveness in papillary thyroid carcinoma. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Clinicopathologic and Diagnostic Significance of p53 Protein Expression in Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma
Mi Kyung Shin, Jeong Won Kim
Asian Pacific Journal of Cancer Prevention.2014; 15(5): 2341. CrossRef
- Clinicopathologic and Diagnostic Significance of p53 Protein Expression in Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma

- Retraction: Clinical Characteristics of Poorly Differentiated Carcinoma of the Thyroid and Comparison of Survival to Tall Cell and Columnar Cell Variants of the Papillary Carcinoma.
- Tae Sik Jung, Jae Hoon Chung, Young Lyun Oh, Tae Yong Kim, Young Kee Shong, Won Bae Kim, Kyung Won Kim, Young Joo Park, Bo Youn Cho
- J Korean Endocr Soc. 2006;21(6):589. Published online December 1, 2006
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/jkes.2006.21.6.589
- 1,642 View
- 26 Download

- Clinical Characteristics of Poorly Differentiated Carcinoma of the Thyroid and Comparison of Its Survival to the Tall Cell and Columnar Cell Variants of Papillary Carcinoma.
- Tae Sik Jung, Jae Hoon Chung, Young Lyun Oh, Tae Yong Kim, Young Kee Shong, Won Bae Kim, Kyung Won Kim, Young Joo Park, Bo Youn Cho
- J Korean Endocr Soc. 2006;21(2):132-141. Published online April 1, 2006
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/jkes.2006.21.2.132
- 1,816 View
- 26 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
Poorly differentiated carcinoma (PDC) of the thyroid includes tall and columnar cell variants (TCV) of the papillary carcinoma as well as the thyroid carcinoma with trabecular, insular and solid (TIS) growth patterns. There have been a few clinical studies on the PDC of the thyroid. We evaluated the clinical characteristics and the outcome of the PDC. METHODS: We investigated the clinicopathologic features of the thyroid carcinoma with TIS growth patterns (n = 46) and TCV of the papillary carcinoma (n = 14). We investigated the clinical features of ten patients diagnosed as PDC of the thyroid who had been undergone thyroidectomy for well differentiated carcinoma previously and compared these outcome with those of patients primarily diagnosed as PDC of the thyroid (n = 60). RESULTS: The clinical course of the thyroid carcinoma with TIS growth patterns was slightly more aggressive than that of TCV of the papillary carcinoma. However, disease-specific survivals of both cancers were not significantly different. Disease-specific survival was independently correlated with the presence of distant metastasis at diagnosis and high dose radioiodine therapy. The clinical features and outcome of the patients with PDC detected at recurred sites after operation for well-differentiated carcinoma were more aggressive than those diagnosed as PDC of the thyroid. CONCLUSION: The prognosis of the thyroid carcinoma with TIS growth patterns and TCV of the papillary carcinoma were similar. The PDC which was detected after thyroidectomy for well-differentiated carcinoma had worse prognosis than primarily diagnosed as PDC of the thyroid.


 KES
KES

 First
First Prev
Prev



